Moodle platform software introduction
Moodle is an open source and free online course management system. Currently, many online schools have established online course systems through this system. The Moodle platform has a simple and elegant interface. Users can adjust the interface and add or delete content at any time as needed. The course list shows the description of each course on the server, including whether visitors are allowed to use it. Visitors can classify and search the courses and learn the courses according to their own needs.
Moodle platform features
1. Course management
Teachers have full control over all course settings, including restrictions on other teachers
You can choose the course format as weekly, topical or community discussion
Flexible course activity configuration - forums, quizzes, resources, polls, questionnaires, assignments, chats, and special discussions
Changes to the course since the last time you logged in can be displayed on the course homepage - making it easier for members to understand what's going on
Most text (resources, forum posts, etc.) can be edited using a WYSIWYG editor
All scores from forums, quizzes and assignments can be viewed on the same page (and can be downloaded as a spreadsheet file)
Comprehensive user logging and tracking - counts each student's activity on the same page, showing graphical reports including details of each module (last access time, number of reads), as well as discussions participated in, etc., compiled for each student detailed "story".
Email Integration - Send discussion board posts, teacher feedback, etc. via email in HTML or plain text format.
Custom Grading Scales - Teachers can define their own grading scales and use them to grade forums and assignments
Use the backup function to package the course into a zip file. This file can be restored on any Moodle server
Moodle platform software advantages
1. Overall design
Moodle is relatively easy to install and can support a large number of courses of various categories. It pays special attention to the security of the entire system. All interfaces are designed in a consistent, simple and efficient style, and require no special browsing skills.
2. Website management
Websites are managed by managers defined during installation. Administrators can enter the "theme" to set the website color, font size, layout, etc. that suits them. There are also activity modules and 43 language packages on the website to meet the needs of learners from different countries. And some codes have been clearly written, making it easy for users to modify them according to their own needs.
3. User management
Each user can choose a language for the Moodle user interface; can specify their own time zone and related data; students are encouraged to create an online profile, including photos, personal descriptions, and email addresses, and this information can be based on User requests are not rendered;
If a learner does not participate in activities for a period of time, the administrator will have a record and their registration will be automatically logged out. For security reasons, teachers can set a login password for the course to prevent unauthorized persons from entering. Course creation accounts are only visible to the people who create and teach those courses.
The goal is to have administrators have as little involvement as possible in the security of the system. Support some verification mechanisms by integrating verification module plug-ins into the system. Students can create their own logins and their email addresses will need to be verified.
2. Job module
You can specify a due date and maximum score for the assignment.
Students can upload assignments (in any file format) to the server - upload times are also recorded.
Late assignments can also be allowed, but teachers can clearly see how late they are
Each assignment of the entire class can be graded (graded and evaluated) on one page and in one form.
Teacher feedback will be displayed on each student's assignment page and will be notified by email.
Teachers can choose whether assignments can be resubmitted for re-grading after grading
3. Chat module
Supports smooth, synchronous text interaction
The chat window contains personal pictures
Supports URLs, smileys, embedded HTML and images, etc.
All conversations are recorded for later review and can also be allowed to be viewed by students
4. Voting module
Kind of like voting in an election. Can be used to vote on something or get feedback from each student (e.g. approval survey)
Teachers can see who chose what in an intuitive table
Optionally allow students to see updated results graphs
5. Forum module
There are several types of forums to choose from, such as teacher-only, course news, open to all, and one topic per user.
Each post features a photo of the author, with image attachments displayed inline
You can browse topics in nested, list, and tree formats, with older or newer posts first.
Everyone can subscribe to a designated forum so that posts will be sent by email. Teachers can also force everyone to subscribe
Teachers can set the forum to be non-replyable (for example, a forum only for posting announcements)
Teachers can easily move topics between forums
If the forum allows ratings, the valid time period can be limited
6. Test module
Teachers can define question banks and reuse them in different tests
Questions can be saved into categories for ease of use, and these categories can be "published" for use in other courses on the same site.
Questions are automatically graded and can be re-graded if the question changes
Possibility to specify opening times for quizzes
Depending on the teacher's settings, the quiz can be attempted multiple times and display feedback and/or correct answers
Questions and answers can be displayed out of order (randomly) to reduce cheating
Questions can contain HTML and images
Questions can be imported from external text files
Quizzes can be attempted multiple times,if desired
If you like, you can complete the test in multiple times, and the results will be automatically accumulated each time.
Multiple-choice questions support one or more answers: including fill-in-the-blank questions (words or phrases), true-false questions, matching questions, random questions, calculation questions (with numerical allowable range), embedded answer questions (cloze style), in the question description Fill in your answers, embed pictures and text descriptions
Various questions designed in Moodle can be backed up and exported, and can be imported into any learning management system that supports international standards.
7. Resource module
Supports display of any electronic document, Word, Powerpoint, Flash, video and sound, etc.
Files can be uploaded and managed on the server, or created dynamically using web forms (text or HTML)
Can connect to external resources on the web or seamlessly incorporate them into course interfaces
Links can be used to pass data to external web applications
Moodle platform installation instructions
(1) Summary description:
The installation steps are relatively simple in summary, mainly including ① moving Moodle files to your Web directory; ② creating a database for Moodle to store all its tables (or selecting an existing database); ③ using a browser to access your Moodle website. You should be taken to the install.php script, which will walk you through creating the config.php file, then setting up Moodle, creating an admin account, etc.; ④ Set up a cron task to call the file admin/cron.php every minute.
(2) Detailed description:
1. Start installing Moodle (the recommended method is to use the command line installer)
Command line installer:
It's best to run the command line as the system's web user. See your system documentation (e.g. "www-data" for Ubuntu/Debian, "apache" for Centos)
Example using command line (as root - substitute "www-data" for your web user):

These tools allow scripting new config.php files. For more information about these options, use
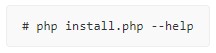
You will be asked for additional settings not discussed on this page - if you are unsure, accept the defaults.
2. If you are unable to do this for some reason (e.g. Windows server), the web-based installer is still available.
Web-based installer:
For ease of use, you can install Moodle over the network. We recommend configuring your web server so that this page is not publicly accessible until the installation is complete.
To run the web installer script, simply go to Moodle's main URL using your web browser.
The installation process will take you through many pages. You should be asked to confirm copyright, view the database tables being created, provide administrator account details and provide site details. Database creation may take some time - please be patient. You should eventually get an invitation to create a new course on the Moodle home page.
You will most likely be asked to download and upload a new config.php file to your Moodle installation - just follow the on-screen instructions.
Introduction to using Moodle platform
1. Basic requirements
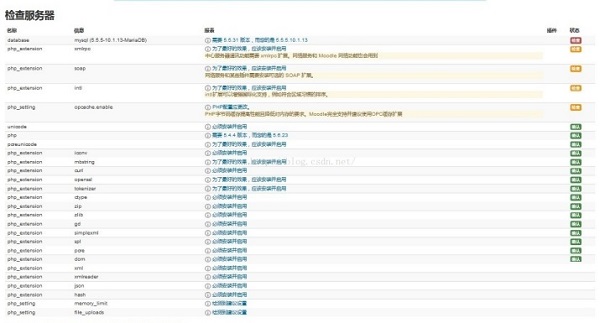
1. You will need a working web server (such as Apache), a database (such as MySQL, MariaDB or PostgreSQL), and configure PHP. Please see the release notes in the dev documentation for software requirements.
2. Moodle requires some PHP extensions. However, Moodle checks early in the installation process and can fix this and restart the installation script if it is missing.
3. If you want Moodle to send email (which you probably do), you will need to run a Sendmail (Unix/Linux) on your server or have access to an SMTP mail server.
2. Create a database
1. Create a new empty database using the database server of your choice. The default encoding must be UTF8. For example, using MySQL:
CREATE DATABASE moodle DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci
2. Create a user/password combination with appropriate permissions for the database.
3. Note: Use GRANT ON GRANT * as include'. *' of the database name and not just the database name is important. Save this password for the Moodle user as you will need it later during installation.
3. Create data directory
1. Create an empty directory to save Moodle files. It cannot be located in the same zone as the web server and must have permissions so that the web server user can write to it. Other than that, it can be located anywhere. Typically, either make it owned by the web server user or give it "Everyone" permissions. If it's on a shared/NFS drive, then with read caching by default, Moodle caches to this disk area and a slow share will mean poor performance.
4. Install Moodle code
1. If you downloaded the zip or tgz file before, then unzip/unzip/move/copy the Moodle code (obtained above) so that it will be served by your web server.
2. Check the permissions to make sure the web server cannot have write permissions to any files in the Moodle code directory (a very common root cause of websites being hacked).
3. If required, configure your web server to serve the Moodle site using a URL of your choice.
5. Configure Moodle
1. In the Moodle code directory, find the config-dist.php file and copy it to a new file called config.php (but read the next step "Installing Moodle" first).
2. Edit config.php with your favorite editor and change the appropriate settings to point to your website, directory, and database. NOTE: The Moodle setup script will create config.php for you if it does not exist, but make sure you set the permissions appropriately (afterwards)
6. Install Moodle
1. Go to the URL of your moodle site in your browser (installation will be done automatically) or run the command line version (requires cli version of PHP):
/usr/bin/php /path/to/moodle/admin/cli/install.php
2. The CLI creates config.php for you. If you created one in the previous step, it will not run.
3. After completing the installation, make sure your file permissions are correct for Moodle program files (not writable by the web server) and Moodle data files (writable by the web server).
7. Set up cron
1. You need to run cron jobs regularly. It is recommended to run cron every minute as required for asynchronous active deletion when using the recycle bin. A typical Unix cron entry is as follows:
* * * * * /usr/bin/php /path/to/moodle/admin/cli/cron.php>/dev/null
2. Unless cron is running regularly, your website will not work properly. It is very important that you do not skip this step.
Moodle platform system configuration requirements
RAM: 256 MB RAM (minimum), 1GB RAM (recommended)
Disk size: 500 MB available fixed disk (more space will be required depending on user uploads)
System requirements for older versions of Moodle:
Windows 98/ME (minimum)
Windows NT / 2000 / XP / 2003 (recommended)
System requirements for Moodle 3.1 and higher:
Windows Vista/7/8/10/2008/2012
PHP requires Microsoft Visual C++ 2015 Redistributable package (download link). This must be the vc_redist.x86.exe download as the PHP build is 32-bit.
Moodle platform update log
1. Fix some bugs;
2. Optimize detailed issues;
Huajun editor recommends:
The Moodle platform is free software, download it if you need it! This site also hasBertso Cloud Academy Student Portal,seewo class optimization master,Spark Thinking Student Terminal,51talk ac online classroom,Xuebajun 1 to 1 teacher version, available for you to download!







































it works
it works
it works