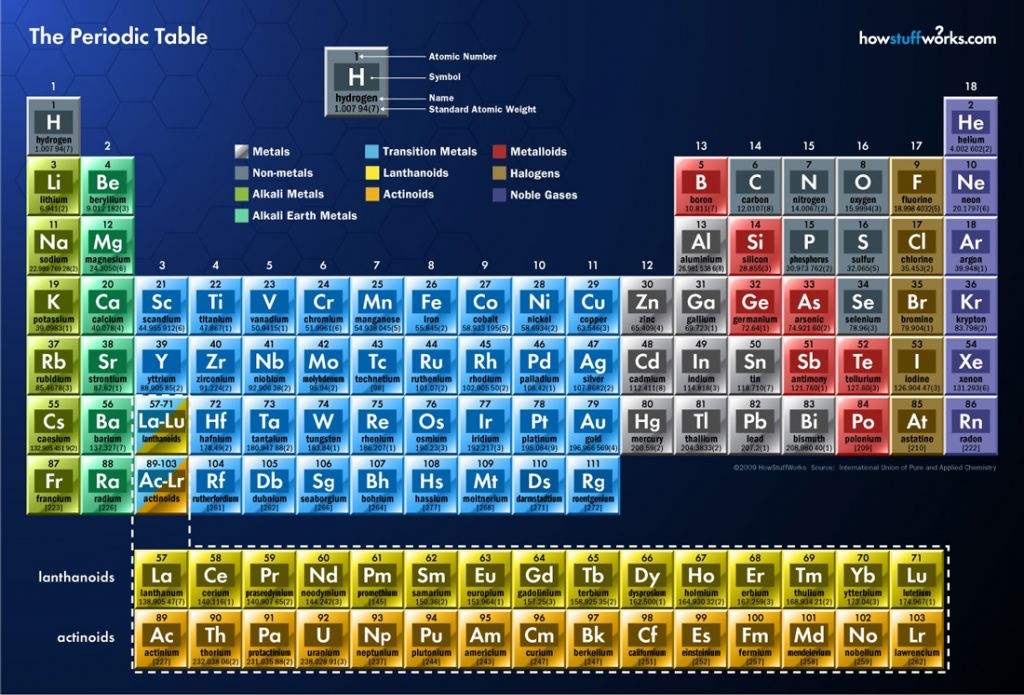
The periodic law of elements in modern chemistry was pioneered by Russian scientist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. He arranged the 63 elements known at that time in the form of a table according to their atomic weight, and placed elements with similar chemical properties in the same OK, this is the prototype of the periodic table of elements. Using the periodic table, Mendeleev successfully predicted the properties of elements that had not been discovered at the time (gallium, scandium, and germanium).
In 1913, the British scientist Moselle used cathode rays to hit metals to produce The arrangement of positive charges (i.e. number of protons or atomic number) took years of revision to become the contemporary periodic table.
In the periodic table, elements are arranged by their atomic number, with the smallest ones listed first. A horizontal row in the table is called a period, and a column is called a family.














































it works
it works
it works