PyDev installation and configuration:
Install PyDev
Before installing PyDev, make sure you have Java 1.4 or higher, Eclipse, and Python installed. Next, start installing the PyDev plugin.
Read the license terms and click Next if you accept them. Enter the installation path selection interface, use the default settings, and then Finish.
Eclipse Update Manager will download PyDev and you can see the progress of the download from the Eclipse taskbar. After downloading, an interface will appear that requires you to confirm whether to install it. Click Install All to start the installation.
After installation, you need to restart Eclipse for the installation to take effect.
Configure PyDev
After installing PyDev, you need to configure the Python/Jython interpreter. The configuration process is very simple.
In the Eclipse menu bar, select Window > Preferences > Pydev > Interpreter - (Python/Jython) to configure the Python/Jython interpreter here. The following uses Python as an example to introduce how to configure.
First you need to add the installed interpreter. Here, Python is installed in the C:Python25 path. Click New, select the Python interpreter python.exe, and after opening, a window containing many check boxes will be displayed. Select the path that needs to be added to the system PYTHONPATH, and click Ok.
Configure PyDev
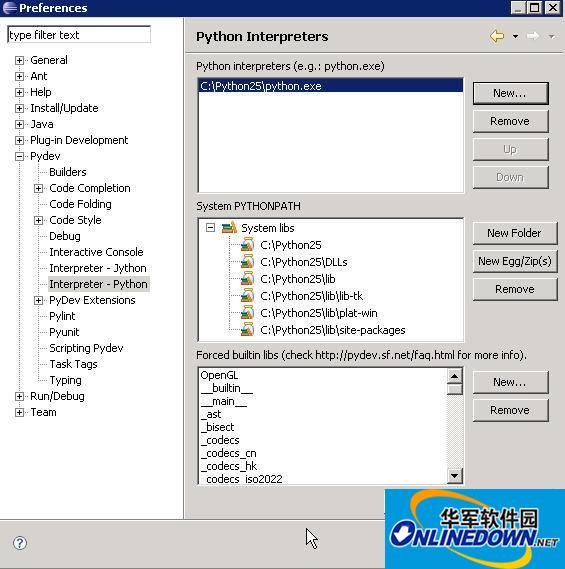
Next, check whether the configuration results are correct.
In System PYTHONPATH, check whether it contains the paths added during the configuration process. All library folders required by the system are listed here.
In addition, Python's built-in libraries are listed in Forced builtin libs. For Python, there are about 50 such built-in libraries, and for Jython, there are about 30.
In this way, the Python interpreter is configured.
PyDev main features:
A Python editor that includes Python syntax highlighting.
Perform Python syntax analysis and highlight errors in the Python editor and Tasks view.
Option to convert tabs to spaces.
The Outline view displays imported libraries, classes, and functions.
Python stack trace information in the terminal view can be hyperlinked to the source code.
Hyperlinks within source code; imports and function calls within the same module can be navigated through hyperlinks.
The ability to run Python scripts from the Navigator view.
The debugger supports breakpoints, stepping through code, and displaying the values of variables.
PyDev options are accessible through Window > Preferences and selecting PyDev (see Figure 1). The first set of options can change how PyDev handles tab characters in source code, and can also change the color of syntax elements.

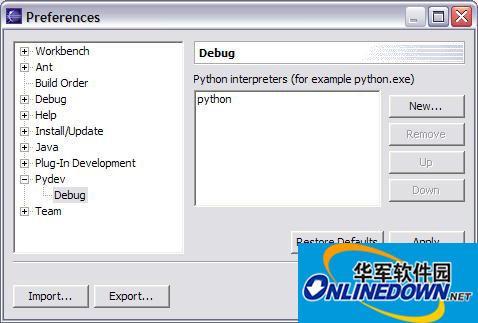
The PyDev Debug option selects the Python interpreter for use when executing Python code. If PyDev cannot find the Python interpreter, or if you want to use a different interpreter, you can set it here (see Figure 2).
Most of my Python work is done in the Resource perspective. To use it, first switch to the Resource perspective, and then double-click the feedParserTest/src/feedparserTest/FeedparserTest.py file in the Navigator view in the upper left corner. The Python editor opens the file, parses the Python syntax, and completes the work of setting colors and syntax checking (see Figure 3).
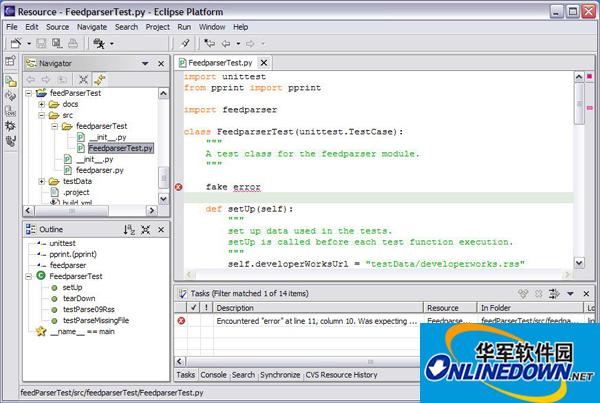
If there are any errors in the source code, they are displayed in the Tasks view in the lower right corner. Double-click the error in the Tasks view to find that pesky line of code.
The Outline view in the lower left corner shows the file currently being edited in an easy-to-browse structure. All imported libraries, classes, and functions are displayed, and navigation can be achieved by double-clicking the item in the Outline view. PyDev aligns pre-parsing work while editing Python files, updates the Outline view, performs syntax checking, and displays syntax elements in different colors.
































Useful
Useful
Useful