Git is simple to learn, has a small size and lightning-fast performance. It outperforms SCM tools like Subversion, CVS, Perforce, and ClearCase with features like cheap local branches, convenient staging areas, and multiple workflows. Different from centralized version control tools such as CVS and Subversion, it adopts a distributed version library approach and does not require server-side software to operate version control, making the release and exchange of source code extremely convenient. Git is fast, which is naturally important for big projects like the Linux kernel. The most outstanding thing about Git is its merge tracing capability.
Function introduction
1. Clone the complete Git repository (including code and version information) from the server to a single machine.
2. Create branches and modify the code on your own machine according to different development purposes.
3. Submit the code on the branch you created on a single machine.
4. Merge branches on a single machine.
5. Fetch the latest version of the code on the server, and then merge it with your main branch.
6. Generate a patch and send the patch to the main developer.
7. Look at the feedback from the main developer. If the main developer finds that there is a conflict between two general developers (a conflict that can be resolved cooperatively between them), they will be asked to resolve the conflict first, and then one of them will submit it. If the lead developer can resolve it himself, or there are no conflicts, pass.
8. Generally, developers can use the pull command to resolve conflicts, and then submit patches to the main developer after the conflicts are resolved.
How to use
1. Create a new folder test locally, right-click after selecting it, and select Git GUI Here

The following picture appears, select the second one to clone the existing warehouse
2. Fill in the Source Location (source address) and Target Directory
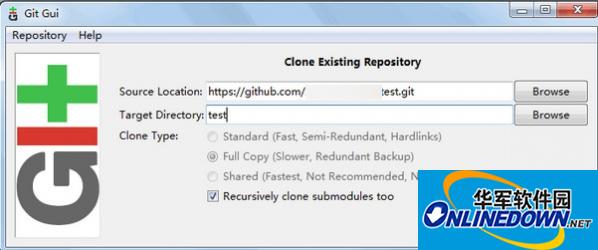
3. Complete cloning
After clicking clone in the picture above, you will be prompted to enter your github username and password. The following interface will appear, and the cloning is completed. You can take a look at the files you cloned locally.





































Useful
Useful
Useful