MATLAB is the abbreviation of Matrix Laboratory, a commercial mathematics software produced by the American MathWorks company. MATLAB is a high-level technical computing language and interactive environment used for algorithm development, data visualization, data analysis, and numerical calculations. It mainly includes MATLAB and Simulink. MATLAB currently only has English and Japanese versions, and no Chinese version is available.
Matlab is a powerful and stable commercial mathematics software released by the mathworks official website. The new version adopts a new view interface and has major updates to MATLAB and Simulink, which can significantly improve the user's use and navigation experience. For example, a new Simulink editor has been added, and a new toolbar has been added to the MATLAB desktop. In addition, the software has redesigned the help system and improved browsing, search, filtering, content classification, etc.
MATLAB FAQ
How to run m-file in matlab?
1. Enter the name of the .m file in the command center (if there are parameters, you need to provide the parameters);
2. Run directly in the .m file editing environment, usually select run in the debug menu item or press F5 directly.
The results of the operation are also displayed in the command center (if you are drawing, it is the figure window)
How to start MATLAB quickly?
MATLAB is a large software. The current 2013 version of the installation package alone reaches 5-6G, so it often starts slowly. This experience introduces three ways to quickly start MATLAB. This experience was completed on a win7 system.
1. Open the run window under win7 system
1. Click Start - Enter the "Run" command (shortcut key: Logo/Windows + R), as shown below
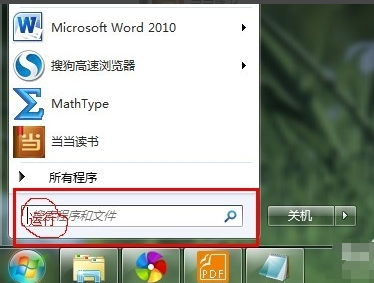
Open the run window and enter the command
In the pop-up "Run" dialog box, enter the "matlab.exe - nojvm" command in it, as shown below.
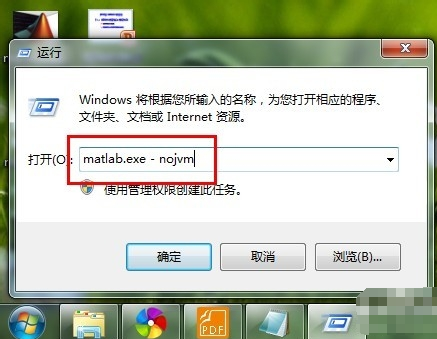
Open the software
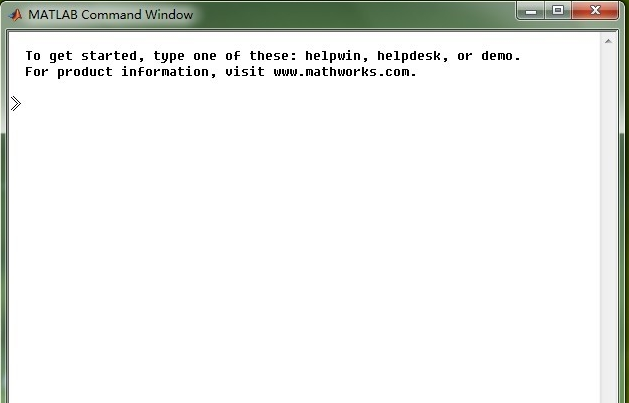
After entering the command in the previous step, press the OK button to open the matlab software. When starting MATLAB, the java virtual machine will be disabled. The MATLAB interface after startup is as shown in the figure below.
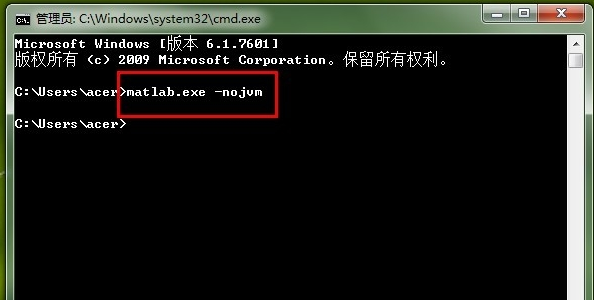
2. Open the DOS window
Click "Start" → "Run" in the computer taskbar to pop up the "Run" dialog box. Enter cmd and enter the MS-DOS window.
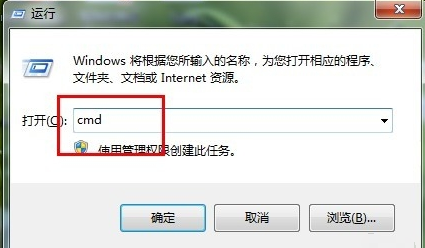
Enter the startup command in the DOS window
Enter the MS-DOS window, and then enter the command "matlab.exe - 4.nojvm". The similarly started matlab will not enable the Java virtual machine. The window after startup is the same as the third step.
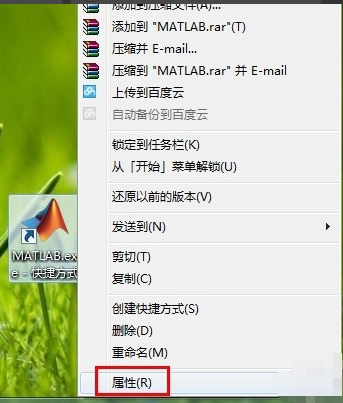
3. Right-click properties of matlab shortcut
For the MATLAB shortcut on the desktop, right-click Properties to open the Properties dialog box.
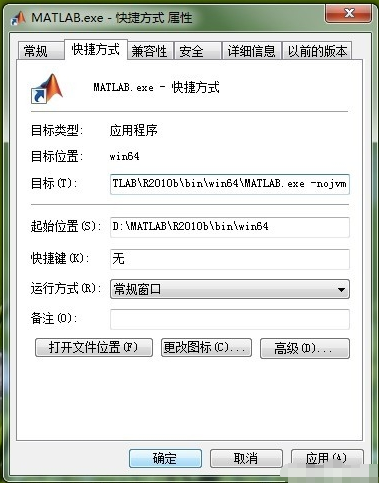
Add startup command to shortcut
Add "-nojvm" in the "Target" column in the "Shortcut" tab and click the "OK" or "Apply" button. Matlab that is also started will not enable the Java virtual machine. The window after startup is the same as the third step.
MATLAB Advantages and Features
1) Efficient numerical calculation and symbolic calculation functions can free users from complicated mathematical operations and analysis;
2) It has complete graphics processing functions to realize the visualization of calculation results and programming;
3) Friendly user interface and natural language close to mathematical expressions make it easy for scholars to learn and master;
4) Function-rich application toolbox (such as signal processing toolbox, communication toolbox, etc.) provides users with a large number of convenient and practical processing tools.
programming environment
MATLAB consists of a series of tools. These tools make it easy for users to use MATLAB functions and files, and many of them use graphical user interfaces. Includes MATLAB desktop and command window, historical command window, editor and debugger, path search, and browser for users to browse help, workspace, and files. With the commercialization of MATLAB and the continuous upgrading of the software itself, the user interface of MATLAB has become more and more refined, closer to the standard interface of Windows, with stronger human-computer interaction and simpler operation. Moreover, the new version of MATLAB provides a complete online query and help system, which greatly facilitates user use. The simple programming environment provides a relatively complete debugging system. The program can be run directly without compilation, and errors can be reported in a timely manner and the cause of the error can be analyzed.
Simple and easy to use
Matlab is a high-level matrix/array language that includes control statements, functions, data structures, input and output, and object-oriented programming features. Users can synchronize input statements and execution commands in the command window, or they can first write a larger and complex application (M file) and then run them together. The new version of MATLAB language is based on the most popular C++ language. Therefore, the grammatical features are very similar to the C++ language, and it is simpler and more in line with the writing format of mathematical expressions by scientific and technical personnel. Make it more conducive to use by non-computer professional technical personnel. Moreover, this language is highly portable and highly scalable, which is also an important reason why MATLAB can penetrate into various fields of scientific research and engineering calculations.
Powerful processing
MATLAB is a collection of numerous computational algorithms. It has more than 600 mathematical operation functions used in projects, which can easily realize various calculation functions required by users. The algorithms used in the functions are the latest research results in scientific research and engineering calculations, and have undergone various optimization and fault-tolerant processing. In general, it can be used in place of low-level programming languages such as C and C++. With the same computational requirements, the programming workload using MATLAB will be greatly reduced. These MATLAB function sets range from the simplest and most basic functions to complex functions such as matrices, eigenvectors, and fast Fourier transforms. The problems that functions can solve generally include matrix operations and the solution of linear equations, differential equations and partial differential equations, symbolic operations, Fourier transform and statistical analysis of data, optimization problems in engineering, sparse matrix operations, various operations of complex numbers, trigonometric functions and other elementary mathematical operations, multi-dimensional array operations and modeling dynamic simulation.
graphics processing
MATLAB has had convenient data visualization functions since its inception to graphically represent vectors and matrices, and the graphics can be annotated and printed. High-level graphics include two- and three-dimensional visualization, image processing, animation, and expression graphics. Can be used for scientific calculations and engineering drawings. The new version of MATLAB has greatly improved and perfected the entire graphics processing function, making it not only more complete in terms of functions that general data visualization software has (such as the drawing and processing of two-dimensional curves and three-dimensional surfaces, etc.), but also has excellent processing capabilities for some functions that other software does not have (such as lighting processing of graphics, chroma processing, and the performance of four-dimensional data, etc.). At the same time, MATLAB also has corresponding functions for some special visualization requirements, such as graphical dialogue, etc., to ensure different levels of user requirements. In addition, the new version of MATLAB also focuses on making great improvements in the production of graphical user interface (GUI), and users with special requirements in this regard can also be satisfied.
module tools
MATLAB has developed powerful module sets and toolboxes for many specialized fields. Generally, they are developed by experts in specific fields, and users can directly use the toolbox to learn, apply and evaluate different methods without writing code themselves. Fields such as data acquisition, database interface, probability statistics, spline fitting, optimization algorithm, partial differential equation solution, neural network, wavelet analysis, signal processing, image processing, system identification, control system design, LMI control, robust control, model prediction, fuzzy logic, financial analysis, map tools, nonlinear control design, real-time rapid prototyping and semi-physical simulation, embedded system development, fixed-point simulation, DSP and communication, power system simulation, etc., all have their own place in the Toolbox family.
Program interface
The new version of MATLAB can use the MATLAB compiler and the C/C++ math library and graphics library to automatically convert your own MATLAB programs into C and C++ code that runs independently of MATLAB. Allows users to write C or C++ language programs that can interact with MATLAB. In addition, the MATLAB web server allows you to use your own MATLAB math and graphics programs in web applications. An important feature of MATLAB is a program extension system and a set of special application subroutines called toolboxes. The toolbox is a subroutine library of MATLAB functions. Each toolbox is customized for a certain discipline and application, mainly including applications in signal processing, control systems, neural networks, fuzzy logic, wavelet analysis and system simulation.
software development
In the development environment, it allows users to control multiple files and graphics windows more conveniently; in terms of programming, it supports function nesting, conditional interrupts, etc.; in terms of graphics, it has more powerful graphics annotation and processing functions, including paired connection annotations, etc.; in terms of input and output, it can directly connect to Excel and HDF5.