OS
Deployer works on a variety of hardware. Universal Deployment technology can deploy and start Windows on different hardware and save technicians from having to configure a new master system for each piece of hardware that requires operating system deployment.
OS Deployer Features
A system disk image can be easily deployed on the hardware on which it was created, or on the same hardware. However, if the motherboard is replaced or a different processor version is used, the deployed system may not boot. Attempting to move a system to a new more powerful computer often yields the same results, as the new hardware is incompatible with the most critical drivers included in the image.
Universal deployment technology provides an effective solution for hardware-independent system deployment by adding key hardware abstraction layers (HAL) and mass storage device drivers.
Customized post-deployment configuration
Not just deploying the image to the target computer. Using the OS Deployer, you can perform post-deployment configuration on target computers, including configuring computer names, domain participation, network settings, and more. In OS
Deployer uses these important post-deployment operations:
User Account: Specify the local user account that needs to be created on the target computer
Computer name: Define the DNS name of the target computer. You can use wildcards to generate unique names
Domain/Workgroup Membership: Receives details of the domain or workgroup to which the target computer belongs
Network settings: Specify the IP address of the target computer and the DNS server IP.
Security Identifier: Generates and assigns a unique security identifier (SID) to the target computer.
Transfer files: Transfer specific files to the target computer
Execute application: Start the service application on the target computer.
Automate your operating system deployment.
Leverage automated operating system image deployment in the following scenarios:
Configuring desktops for new employees.
Redeploy corrupted PC operating systems to save troubleshooting time
Organizational policy to regularly redeploy the operating system
OS Deployer support system
Windows XP Professional SP2
Windows XP Professional x64 Edition
Windows XP Professional Edition
Windows XP Home
Windows Vista Ultimate (x86, x64)
Windows Vista Business Edition (x86, x64)
Windows Vista Home Premium (x86, x64)
Windows Vista Home Basic (x86, x64)
Windows 2000 Professional SP4
Windows 2000 Advanced Server
Windows 2000 Server
Windows Server 2003 x64 version
Windows Storage Server 2003 R2
Windows Small Business Server 2003
Windows Small Business Server 2011
Windows Server 2003 R2 (x86, x64)
Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2 (x86, x64)
Windows Server 2008 (x86, x64)
Windows 2008 R2
Windows 7
Windows 8 (x86, x64)
Windows 8 Pro (x86, x64)
Windows 8 Enterprise (x86, x64)
Windows 10 Home Page (x86, x64)
Windows 10 Professional (x86, x64)
Windows 10 Enterprise (x86, x64)
Windows 10 Education (x86, x64)
Windows 2012 (Foundation, Essential, Standard and Datacenter)
Windows NT/4.0 Server
Windows 98/Me
OS Deployer Features

Manual deployment
Consider a scenario -
You received new hardware for which you don't know the MAC address. When installing the operating system on these computers, you will need to use ManageEngine bootable media or ManageEngine PXE(P reboot
e
nvironment) server manually changes the startup order of all computers to the ManageEngine environment before the created image can be deployed. Deployment configuration can be set in the deployment template or manually configured when deploying the image.

Event-driven deployment
Event-driven deployment is ideal for situations where you need to deploy an OS to multiple systems simultaneously and control bandwidth during deployment. Administrators can configure to initiate deployment when predefined computers are ready for deployment, after which the operating system image is multicast to all target computers. Optionally, administrators can also set a timeout period after which the deployment will begin regardless of whether the predefined number is reached.

Scheduled deployment
Scheduled deployments are ideal for situations where you need to deploy an OS to multiple systems with a list of known MAC addresses. For example, if you receive a batch of 100 new computers and their MAC addresses that need to be deployed nightly, you can schedule deployment by specifying a list of MAC addresses. OS
Deployer will use the Wake On LAN feature to power on the computer and deploy the image at the scheduled time.

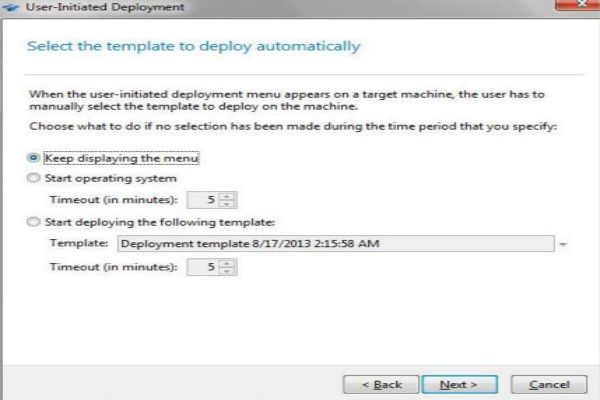
Custom deployment
Custom deployments are initiated by the user. Administrators create a set of deployment templates that meet the needs of the organization and assign each template a name that users can easily understand. Administrators create bootable media or PXE packages containing templates and switch sets in custom deployment mode. Users who need to redeploy their computers boot the computer from bootable media or PXE and select the template by name from the boot menu. Deployment starts immediately and occurs independently on each computer.

Independent deployment
Independent deployment is a computer deployment on the Internet.
Deployment that cannot be accessed by the server. Perform standalone deployments locally using the bootable ManageEngine Standalone Utility.
OS Deployer update log
1.Fix BUG, the new version has a better experience
2. Some pages have been changed
Huajun editor recommends:
The editor of OS Deployer personally inspected it and found it to be true! This site also has similar software Kaspersky Total Security Software, .NET, and Cloud Machine Manager. Welcome to click to download and experience it!