There are two types of hard drives in computers, one is a solid-state drive and the other is a traditional mechanical hard drive. Their main functions are used to store data, information and other information. It is understood that there are many types of solid-state drives, so some users do not If you know what kind of interface SSD you are using, let’s take a look at it below.
What is the interface of solid state drive?
In fact, solid-state drives have several interfaces, and solid-state drives generally have different interfaces according to different applications. Compared with traditional mechanical hard drives, solid-state drives have many interface specifications and are easily confused by first-time users. The following are introduced below:
Mainstream commonly used--SATA interface
The SATA interface is no longer a new technology. From the launch of SATA 1.0 in 2001 to the current SATA2.0 and SATA3.0, SATA has become the main interface of current solid-state drives. In terms of current usage, SATA2.0 still has the most users, which is mainly affected by the PC interface. However, most of the SATA3.0 products currently on the market are backward compatible with 2.0.

SATA interface
SATA interface solid-state drives are mostly used to replace mechanical hard drives. Our desktop upgrades mainly use this type of interface. With the successive introduction of SATA 2.0 and 3.0, the transmission rate has doubled to 300 and 600MB/s. This is the earliest PATA interface, which is incomparable to the IDE interface.
Although SATA 2.0 is the mainstream SSD interface at this stage, and SATA 3.0 accounts for a lower proportion, its transfer rate of up to 600MB per second is destined to become the future interface trend of SSD.
There are many server types-PCI-E interface
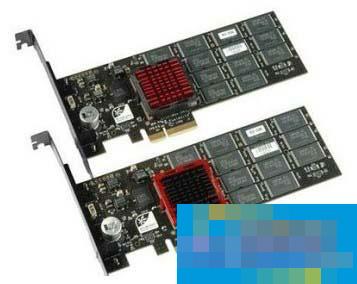
PCI-E interface
Compared with the SATA interface that everyone has more contact with, PCI-E is mainly used for embedded applications. Although SSDs replace the low speed of mechanical devices with physical devices compared to mechanical hard drives, in the process of performance improvement, SSDs are again limited by physical size and data interfaces. The PCI-E interface has greater bandwidth than SATA, which can further improve performance and capacity and fully unleash the potential of solid-state drives.
Although there are many PCI-E interface motherboards on the market, due to price and ease of use, PCI-E interface SSDs are mostly used in servers. The transfer rate of PCIe 2.0 has been increased from the one-way 250MB/s of PCIe 1.0 to 500MB/s, and PCI 3.0 can be increased to 750MB/s, which is more exciting than SATA.
If we look at the ×16 specifications adopted by high-end display adapters, PCIe 2.0 can achieve a one-way transmission rate of 8GB/s, and PCIe 3.0 can achieve a one-way transmission rate of 12GB/s. Very suitable for professional personnel use.
Exclusively for Macintosh--LIF interface SSD
If you are using an Apple brand machine and want to use a solid-state drive, the first choice is the LIF interface and then consider the price and capacity issues. I won’t go into details. At present, the LIF interface SSDs on the market are mainly Yuanke products, while other brands are mostly disassembled products with little market circulation.

The above is how to view the solid state drive interface? What types of solid state drive interfaces are there? content, I hope it can help you.