A differential disk is created with a VHD as the master disk, with read operations mapped to the master disk and write operations directed to its own VHD. The differential disk is also called the child (differential) VHD, and the mother disk is also called the parent (mother) VHD.
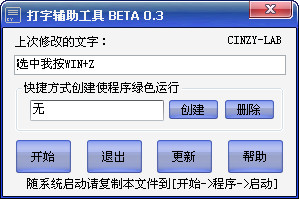
The Windows VHD auxiliary processing tool is an auxiliary tool for creating, installing, and maintaining VHD. It simplifies a relatively complex operation process and allows you to easily experience the powerful functions of VHD. Including: creating VHD, installing Windows 7 system into VHD, creating differential VHD, merging VHD, mounting and detaching VHD, adding VHD project to BCD, deleting VHD project from BCD, and quick replacement of differential VHD, etc. Built-in ImageX.exe and Ghost32.exe support loading WIM or GHO system into VHD.
System requirements: Windows 7/8, Windows Server 2008 R2, WinPE 3.0
Using differential VHD, you can achieve the effect of restoring software and virtual machines. Multi-level differential is equivalent to creating multiple restore points.
Basic operation process:
1. Create VHD
2. Create differential VHD
3. Add VHD project to BCD
- Green versionView
- Green versionView
- Green versionView
- Green versionView
Function introduction
The main new features of the VHDX format are as follows:
Supported virtual hard disks with storage capacities up to 16 TB.
By logging updates to VHDX metadata structures, you can protect data from corruption in the event of a power failure.
Improved alignment of virtual hard disk format to work better on large sector disks.
The VHDX format also provides the following features:
The larger block sizes of dynamic disks and differential disks allow these disks to meet workload demands.
A 4 KB logical sector virtual disk that provides high performance when used by applications and workloads designed for 4 KB sectors.
Ability to store custom metadata about files that users may want to log, such as operating system versions or applied patches.
Efficiently represent data (also known as "clipping"), making file sizes smaller and allowing the underlying physical storage device to reclaim unused space. (Trimming requires a physical disk attached directly to the virtual machine or a SCSI disk and trim-compatible hardware.)











































Useful
Useful
Useful