
Git software introduction
Git is a free, open source distributed version control system used to handle any project, small or large, with agility and efficiency. Git is a version control tool used for Linux kernel development. Different from centralized version control tools such as CVS and Subversion, it adopts a distributed version library approach and does not require server-side software to operate version control, making the release and exchange of source code extremely convenient. Git is fast, which is naturally important for big projects like the Linux kernel. The most outstanding thing about Git is its merge tracking (merge tracing) capability.
Git software features
Distributed
One of the best features of any distributed SCM (including Git) is that it is distributed. This means that instead of "checking out" the current tip of the source code, you "clone" the entire repository.
Multiple backups
This means that even if you are using a centralized workflow, each user essentially has a full backup of the main server. In the event of a crash or corruption, each of these replicas can be pushed up to replace the primary. In fact, Git has no single point of failure unless there is only one copy of the repository.
Any workflow
Because of Git’s distributed nature and excellent branching system, nearly endless workflows can be implemented with relative ease.
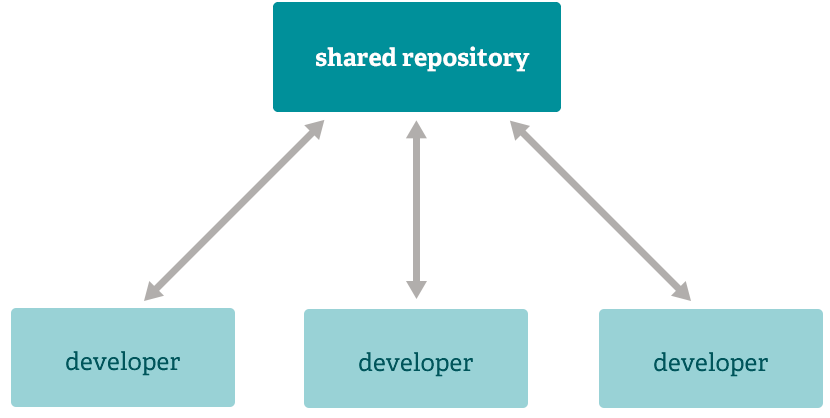
Subversion style workflow
Centralized workflows are very common, especially among people transitioning from centralized systems. Git will not allow a push if someone has pushed since the last scrape, so a centralized model with all developers pushing to the same server can work well.
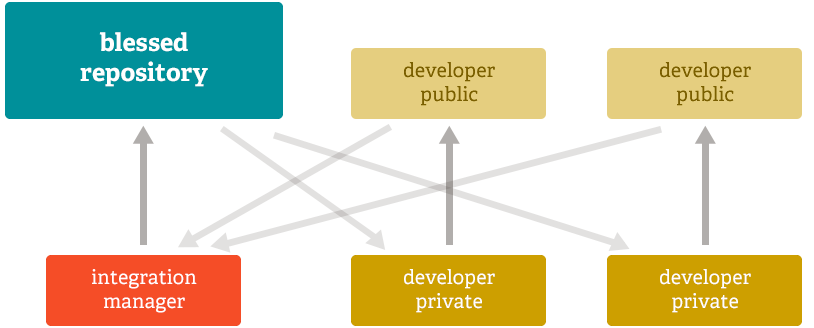
Integration Manager workflow
Another common Git workflow involves an integration manager – a person who works on a “sacred” repository. Many developers then clone from that repository, push to their own independent repositories, and ask the integrator to bring in their changes. This is the type of development model common in open source or GitHub repositories.
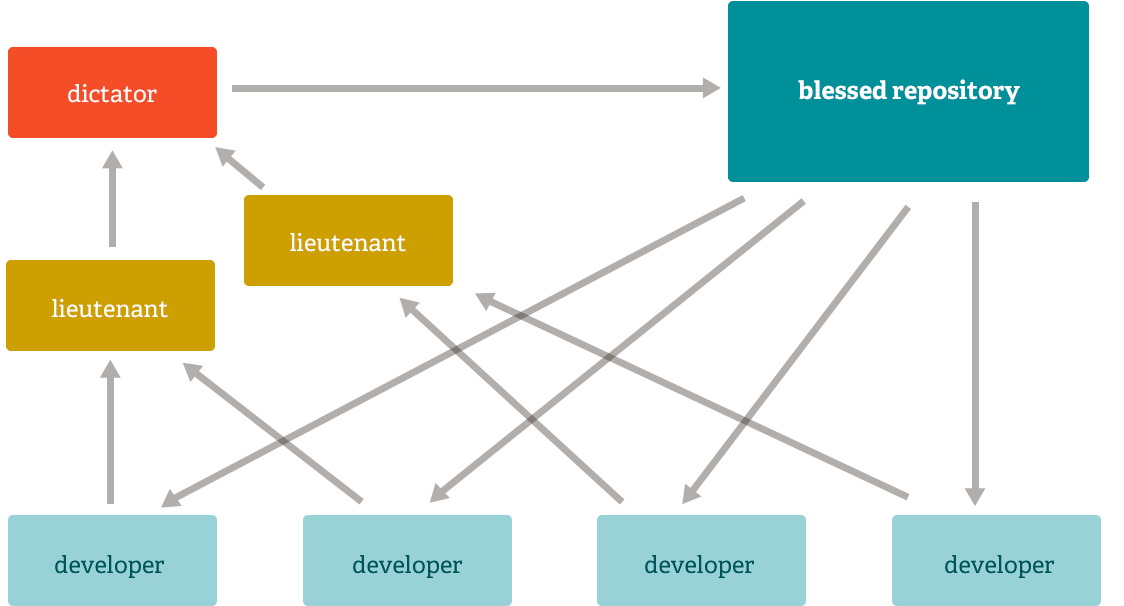
Dictator and Lieutenant Workflow
For larger projects, a development workflow like that of the Linux kernel is often effective. In this model, a few people ("deputies") are responsible for a specific subsystem of the project, and they are incorporated into all changes related to that subsystem. Another integrator (the "dictator") can just take changes from his/her deputies and push to the "blessed" repository from which everyone can clone again.
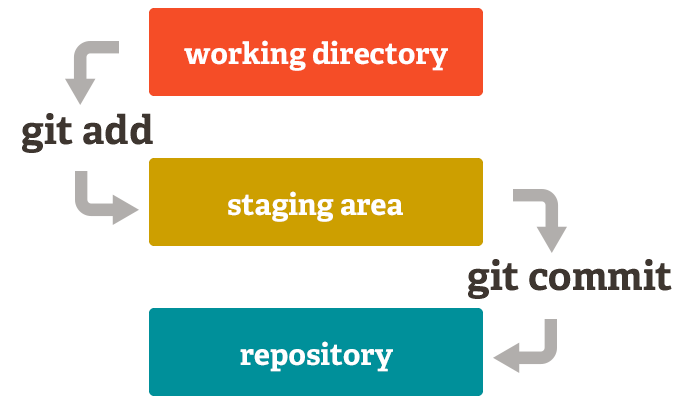
Git software features
Unlike other systems, Git has something called a "staging area" or "index". This is an intermediate area where the submission can be formatted and reviewed before it is finalized.
What makes Git different from other tools is that it can quickly stage a few files and commit them without committing all other modified files in the working directory or listing them on the command line during the commit process.
This allows you to stage only part of a modified file. Gone are the days of making two logically unrelated changes to a file before realizing you forgot to commit one of the files. Now you only need to prepare the required changes for the current commit and other changes for the next commit. This feature can make as many different changes to a file as needed.
Of course, if you don't want that kind of control, Git is also very easy to ignore this feature - just add a "-a" to the commit command to add all changes to all files to the staging area.
Git change log
1: Optimized performance
2: We are serious about solving bug problems
Huajun editor recommends:
Git is one of the best software in the industry. I believe that many friends will have used it. If you don’t use it anymore, you will be OUT. This site also prepares for youMaven,OpenCart,Java2 Runtime Environment,GCC For Linux,Free Pascal






































Useful
Useful
Useful